Projectile Motion
Projectile Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Projectile Motion, Vertical Motion, Condition for Projectile Hitting Inclined Plane Horizontally & Projectile Motion from a Moving Plane etc.
Important Questions on Projectile Motion
A ball is projected at an angle of above with the horizontal from the top of a tower and strikes the ground in at angle of with the horizontal. Find the height of the tower and the speed with which it was projected.
A particle is projected in the X-Y plane. after projection, the velocity of the particle makes an angle with the X-axis. after projection, it moves horizontally. Find the velocity of projection (use )
A particle is projected in x-y plane with y-axis along vertical, the point of projection being origin. The equation of projectile is . The angle of projectile is ---------------------- and initial velocity is -----------------------------------
A rifle with a muzzle velocity of shoots a bullet at a small target away in the same horizontal line. How high above the target must the gun be aimed so that the bullet will hit the target?
Two bodies of same mass are projected with the same velocity at an angle and respectively. The ratio of their horizontal ranges will be
The maximum range of a gun of horizontal terrain is . If then, muzzle velocity of a shell must be
From a high building, a stone is dropped and simultaneously another identical stone is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of Which one of the following statements is true?
A bullet is fired horizontally from a gun with a speed of in order to hit a target away. From what height above the target should the gun be aimed? (The resistance of air is negligible and ,
An object is kept fixed at the point and on a plank raised above the ground. At time the plank starts moving along the direction with an acceleration At the same instant a stone is projected from the origin with a velocity as shown. A stationary person on the ground observes the stone hitting the object during its downward motion at an angle of to the horizontal. All the motions are in the plane. Find and the time after which the stone hits the object. Take
A large heavy box is sliding without friction down a smooth plane of inclination . From a point on the bottom of the box, a particle is projected inside the box. The initial speed of the particle with respect to the box is and the direction of projection makes an angle with the bottom as shown in the figure:
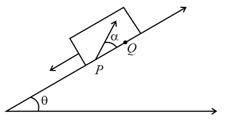
If the horizontal displacement of the particle as seen by an observer on the ground is zero, find the speed of the box with respect to the ground at the instant when the particle was projected.
A large heavy box is sliding without friction down a smooth plane of inclination . From a point on the bottom of the box, a particle is projected inside the box. The initial speed of the particle with respect to the box is and the direction of projection makes an angle with the bottom as shown in the figure:
Find the distance along the bottom of the box between the point of projection and the point where the particle lands. [Assume that the particle does not hit any other surface of the box. Neglect air resistance]
Two guns situated on the top of a hill of height fire one shot each with the same speed at some interval of time. One gun fires horizontally and other fires upwards at an angle of with the horizontal. The shots collide in air at point . Find the time interval between the firings.
A projectile can have the same range for two angles of projection. If and be the times of flights in the two cases, then the product of the two time of flights is proportional to –
A projectile can have the same range ‘R’ for two angles of projection. If ‘t1’ and ‘t2’ be the times of flight in the two cases, then the product of the two times of flight is proportional to
A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a speed of at an angle of with the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the ball be at the height of 10 m from the ground? [Take g = 10 ms-2]
When two projectiles are fired from complementary angles having times of flight and maximum heights respectively, which of the following is incorrect?
A body of mass is projected with a velocity making an angle with horizontal. Its horizontal range is . The body splits into two equal parts at the highest point and one of the particle comes to rest. Then, the horizontal distance travelled by the other particle from the point of projection is
Ifbe the horizontal range andbe the maximum height attained by a projectile then velocity of projection is
A particle of mass is projected from the origin on ground with the speed of at an angle of with the horizontal. Consider no air resistance. The particle does a projectile motion and falls back on the ground. The average torque in due course of motion on the particle w.r.t. the observer at the origin is
A particle projected with a velocity , from a vertical wall. After striking the wall it lands at
